Pneumonia
 |
Pneumonia |
What is pneumonia (meaning)
Pneumonia is defined as acute inflammation of the lungs parenchyma distal to the terminal bronchioles consisting of the respiratory bronchioles,alveoli,alveolar sac .The term pneumonia and pneumonitis are often used synonymously for inflammation of the lungs while consolidation meaning "solidification" is the term used for gross and radiologic appearance of the lungs in pneumonia.
Classification(Types of pneumonia)
On the basis of Anatomical region of the lung parenchyma involved-
- Lobar pneumonia
- Bronchopneumonia
- Interstitial pneumonia
Based on clinical settings in which infection occurred
1.Community acquired pneumonia
2.Healthcare associated pneumonia
3.Ventilator-associated pneumonia
Based on etiology and pathogenesis
1.Bacterial pneumonia
2.Viral pneumonia
3.Pneumonia from other etioloy
Pathogenesis (causes of pneumonia)
1.The microorganism gain entry into the lungs by one of the following four routes
2.Inhalation of microbes present in the air
3.Aspiration of organism from nasopharynx and oropharynx
4.Hematogenous spread from a distant focus of infection
5.Direct supplied from an adjoining site of infection
1. Stage of congestion:Initial Phase
2. Red Hepatisation: Early Consolidation
3. Grey Hepatisation: Late consolidation
4. Resolution
Lab diagnosis of Pneumonia
A. Specimens
1. Sputum
2.Blood
3.Pleural fluid
4.Blood for serological test
B. Direct microscopy
1.Gram staining
2.Ziehl-neelsen staining
3.Giemsa staining
C. Culture
Sputum ,blood and pleural fluid can be cultured on the blood Agar and chocolate Agar. Purulent portion of sputum is best for culture. If the sputum is too viscid,it may be homogenised.
Media for culture-
Blood Agar
Chocolate Agar
Lowenstein Jensen media
Selective media
D. Detection of bacterial antigens
Direct immunofluorescence test direct immunofluorescence examination of sputum is done to detect antigen in L.pneumophilla.
E. Serology
Diagnosis of some causative organism is made by a demonstration of antibody in patients serum. Most often these are diagnosed by High titres in a single sample, But demonstration of a four fold rise in titre of antibody is better.
1.Mycoplasma pneumoniae
2.Chlamydophila pneumoniae
3.Legionella pneumophilla
4.Coxiella burnetii
F. Chest X-Ray of Pneumonia
Failure of Defence mechanism and presence of certain predisposing factors result in pneumonia. These conditions are as under
1.Altered consciousness
2.Depressed cough and gllotic reflexes
3.Impaired mucociliary transport
4.Impaired alveolar macrophage function
5.Endobronchial obstruction
6.Immunocompromised state
Symptoms of pneumonia
- Cough, which may produce greenish, yellow or even bloody mucus.
- Fever
- Sweating and shaking chills.
- Shortness of breath.
- Loss of appetite
- Low energy
- Rapid, shallow breathing.
- Sharp or stabbing chest pain that gets worse when you breathe deeply or cough.
- Fatigue
Treatment of pneumonia
Treatment for pneumonia involves curing the infection.
- Antibiotics. These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and to choose the best antibiotic to treat it.
- Cough medicine. This medicine may be used to calm your cough. Because coughing helps loosen and move fluid from your lungs, it's a good idea not to eliminate your cough completely. If you want to try a cough suppressant, use the lowest dose that helps you rest.
- Fever reducers/pain relievers. for lowering fever and discomfort.
Vaccine for pneumonia
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13): Given to children and adults. It helps to prevent pneumococcal disease.
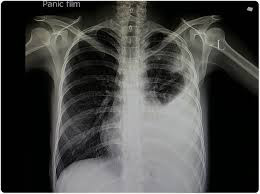
Pneumonia chest X-ray
showing Lung inflammation
Consolidation
Hydrothorax
pneumonia in corona(COVID-19)
Most people who get COVID-19 have mild or moderate symptoms of pneumonia like cough,wheezing,fever, and shortness of breath,dysapnoea. But some patient with coronavirus get severe pneumonia in lungs.
Lobar pneumonia
Lobar pneumonia is an Acute bactarial infection of a part of a lobe,entire lobe,or even two lobe or both the lungs.
Lobar pneumonia causes(etilogy)
Based on etiologic microbial agent causing lobar pneumonia ,following types of lobar pneumonia are described:
1.Pneumococcal pneumonia :
More than 90% of all lobar pneumonias are cause by streptocoocus pneumonae,a lancet-shaped diplococcus.
2.Staphylococcal pneumonia:
Staphylococcus aureus causes pneumonia by haemotogenous spread of infection from another focus or after viral infection.
3.Streptococcal pneumonae:
Beta-haemolytic streptococci may rarely cause pneumonia such as in children after measles or influenza,in severly debilitated elderly patient and in diabetics.
4.Pneumonia by gram-negative aerobic bacteria:
Less common cause in children below 3yrs of age after a preceding viral infection.
Symptoms and signs:
- Cough, with greenish, yellow or even bloody mucus.
- Fever
- sweating and shaking chills.
- Shortness of breath.
- Rapid, shallow breathing.
- Sharp or stabbing chest pain
- Loss of appetite
- Low energy, and fatigue.
Lobar pneumonia Treatment
Administration of cefoperazone/sulbactam combined with azithromycin for treating children and could be used as the first choice of treatment for lobar pneumonia. Cefoperazone/sulbactam, which has strong antibacterial properties.
Azithromycin has been shown to have significant therapeutic effects on infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae .
Lobar pneumonia chest X-Ray

Lower lobe lober Pneumonia

